What is Ontology?
Ontology is the philosophical study of the nature of being, existence, or reality, as well as the basic categories of being and their relations. Traditionally listed as a part of the major branch of philosophy known as metaphysics, ontology deals with questions concerning what entities exist or may be said to exist and how such entities may be grouped, related within a hierarchy, and subdivided according to similarities and differences.
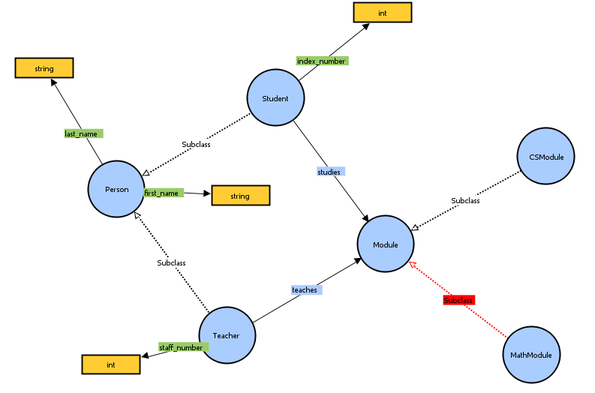
A good ontology is needed in order to provide a consistent and accurate representation of a domain of knowledge. It is also needed in order to enable reasoning within that domain and to support the automated manipulation of data within that domain. The below picture is described in [1].
The aim is to represent what it was intended to represent(the domain). The designed ontology should have maximal coverage and great precision of the domain to be called as a good ontology.
Knowledge Graph and Ontology:
A knowledge graph is a model for representing structured data that can be used to describe real–world entities and their relationships. Knowledge graphs are used to represent and store data in a graph–like format, where nodes represent entities and edges represent relationships between entities. On the other hand ontologies are used to represent and store data in a structured way, where entities are represented as concepts and relationships between entities are represented as properties. There is a one–to–one correspondence between entities in a knowledge graph and concepts in an ontology. In other words, each entity in a knowledge graph corresponds to a concept in an ontology, and each relationship between entities in a knowledge graph corresponds to a property in an ontology.
Why both are important?
There are a few reasons for this. First, knowledge graphs and ontologies provide structure for data. This can make it easier for machines to process and understand the data. Second, they can help with data integration. By providing a common framework for data, they can make it easier to combine data from different sources. Finally, they can help with decision support. By providing a way to formalize knowledge, they can help decision-makers find the best course of action.

There are various tools available to make ontology maintenance easier. Some of these tools are listed below:
– Protégé: A free, open–source ontology editor and framework for building intelligent systems.
– TopBraid Composer: A commercial ontology editor from TopQuadrant.
– OntoText GraphDB: A commercial ontology database from OntoText.
– Semantic Web Company PoolParty: A commercial ontology management platform from Semantic Web Company.
There are many tools that can be used to generate knowledge graphs. Some of these tools are: 1. RDF2Graph 2. Semantic Web Rule Language 3. Web Ontology Language 4. RDF Graph Pattern 5. SPARQL 6. GraphQL 7. Neo4j 8. AllegroGraph 9. Stardog 10.Ontotext GraphDB
There are many more but one of the most popular is neo4j. There are a few reasons why Neo4j is so popular:
1. It is one of the most mature graph databases on the market, with a wide range of features and capabilities.
2. It has a large and supportive community, with many resources available to help users get the most out of the database.
3. Neo4j is highly scalable, meaning it can handle large amounts of data and complex queries with ease.
4. It is relatively easy to learn and use, compared to other graph databases.
5. Neo4j is backed by a well–established company, ensuring that it will continue to be developed and supported in the future.


